18. Java modules and libraries¶
deegree webservices is a Java web application and based on code written in the Java programming language. As a user, you usually don’t need to care about this, unless you want to extend the default functionality available in a deegree webservices setup. This chapter provides some basic knowledge of JAR (Java archive) files, the Java classpath and describes how deegree webservices finds JARs. Additionally, it provides precise instructions for adding JARs so your deegree webservices instance can connect to Oracle Spatial and Microsoft SQL Server databases.
Hint
The terms JAR, module and library are used interchangeably in this chapter.
18.1. Java code and the classpath¶
Java code is usually packaged in JAR files. If you want to extend deegree’s codebase, you will have to add one or more JAR files to the so-called classpath [1]. Basically, there are two different types of classpaths that determine which JAR files are available to deegree webservices:
- The web application classpath
- The workspace classpath
The full classpath used by deegree webservices consists of the web application classpath and the workspace classpath. If conflicting files exist on both classpaths, the file on the workspace classpath takes precedence.
Tip
If you’re not familiar with classpath concepts and don’t have any special requirements, simply add your JAR files to the workspace classpath and ignore the web application classpath.
18.1.1. Web application classpath¶
As deegree webservices is a Java web application, standard paths apply:
- Directory WEB-INF/lib of the deegree web application (for JARs)
- Directory WEB-INF/classes of the deegree web application (for Java class files)
- Global directories for all web applications running in the container (depends on the actual web container)
When you add files to the web application claspath, you have to restart the web application or the web application container to make the new code available to deegree webservices.
Hint
All Java libraries shipped with deegree webservices are located in the WEB-INF/lib directory of the deegree webservices webapp. If you downloaded the ZIP version, this directory is located in webapps/ROOT/WEB-INF/lib.
18.1.2. Workspace classpath¶
When deegree webservices initializes the workspace, it scans directory modules/ of the active deegree workspace for files ending with .jar and adds them to the classpath. This can be very handy, as it allows to create self-contained workspaces (no fiddling with other directories required) and also has the benefit the you can reload the deegree workspace only after adding your libraries (instead of restarting the deegree webapp or the whole web application container).
Hint
In addition to workspace directory modules/, directory classes/ can be used to add individual Java classes (and other files) to the classpath. This is usually not required.
Since deegree 3.4 jdbc drivers are not longer loaded from workspace classpath. Instead deegree follows the commonly used method to only use jdbc drivers which are available either by the system (shared or server libraries) or by the application (WEB-INF/lib).
18.2. Checking available JARs¶
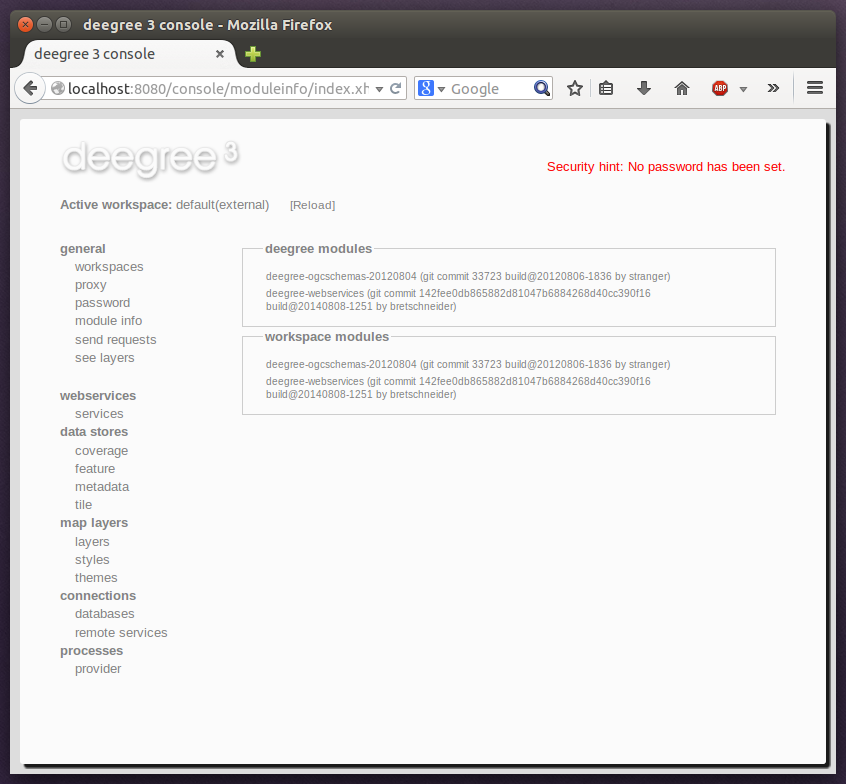
In order to see which JARs are available to your deegree webservices instance/workspace, use the “module info” link in the general section of the service console:
The list of JARs section displays the JARs found on the web application classpath, while the lower section displays the JARs found on the workspace classpath.
18.3. Adding database modules¶
By default, deegree webservices includes everything that is needed for connecting to PostgreSQL/PostGIS and Derby databases. If you want to connect to an Oracle Spatial or Microsoft SQL Server instance, you need to add additional Java libraries manually, as the required JDBC libraries are not included in the deegree webservices download (for license reasons).
18.3.1. Adding Oracle support¶
The following deegree resources support Oracle Spatial databases:
- SimpleSQLFeatureStore
- SQLFeatureStore
- ISOMetadataStore
In order to enable Oracle connectivity for these resources, you need to add two JAR files (see Java code and the classpath):
18.3.2. Adding Oracle GeoRaster support¶
The OracleGeoraster coverage store supports GeoRaster Objects stored in Oracle databases.
In order to enable Oracle connectivity for these resources, you need to add the following JAR files (see Java code and the classpath):
- A compatible Oracle JDBC-type driver [2] * ojdbc8.jar
- The Oracle Spatial and GeoRaster libraries and their dependencies * sdoapi.jar * sdogr.jar * sdotype.jar * sdoutl.jar * xdb6.jar * xmlparserv2_sans_jaxp_services.jar
- Module deegree-coveragestore-oracle-georaster [6]
Hint
The Oracle Spatial and GeoRaster libraries can be found, without version number in filename, inside the Oracle Database installation directory. The sdo* files can be found at ORACLE_HOME/md/jlib, xdb6.jar at ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib and xmlparserv2_sans_jaxp_services or xmlparserv2 at ORACLE_HOME/xdk/lib.
Note
The xmlparserv2_sans_jaxp_services is the recommended library, as it does not contain META-INF/services/ entries. But if this library is not available the xmlparserv2 can be used instead. (In rare conditions this could set the oracle library as default XML parser, which could lead to unexpected behavior).
18.3.3. Adding Microsoft SQL server support¶
The following deegree resources support Microsoft SQL Server:
- SimpleSQLFeatureStore
- SQLFeatureStore
- ISOMetadataStore
In order to enable Microsoft SQL Server connectivity for these resources, you need to add two JAR files (see Java code and the classpath):
Footnotes
| [1] | The term classpath describes the set of files or directories which are used to find the available Java code (JARs and class files). |
| [2] | (1, 2) http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/features/jdbc/index-091264.html (registration required) |
| [3] | http://repo.deegree.org/content/repositories/public/org/deegree/deegree-sqldialect-oracle/3.4.2/deegree-sqldialect-oracle-3.4.2.jar |
| [4] | http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/sqlserver/aa937724.aspx |
| [5] | http://repo.deegree.org/content/repositories/public/org/deegree/deegree-sqldialect-mssql/3.4.2/deegree-sqldialect-mssql-3.4.2.jar |
| [6] | http://repo.deegree.org/content/repositories/public/org/deegree/deegree-coveragestore-oracle-georaster/3.4.2/deegree-coveragestore-oracle-georaster-3.4.2.jar |